Podiatry Weekly is owned and operated by Marat Kazak DPM. All information presented here is for educational purposes only and is not meant to be taken or used as medical advice. Always consult with your doctor before starting or changing your medical therapy or exercise routine. Podiatry Weekly is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program and other affiliate programs. We are compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies. We may earn money or products from the companies mentioned in this post.

Leviticus 17:11: “For the life of the flesh is in the blood”
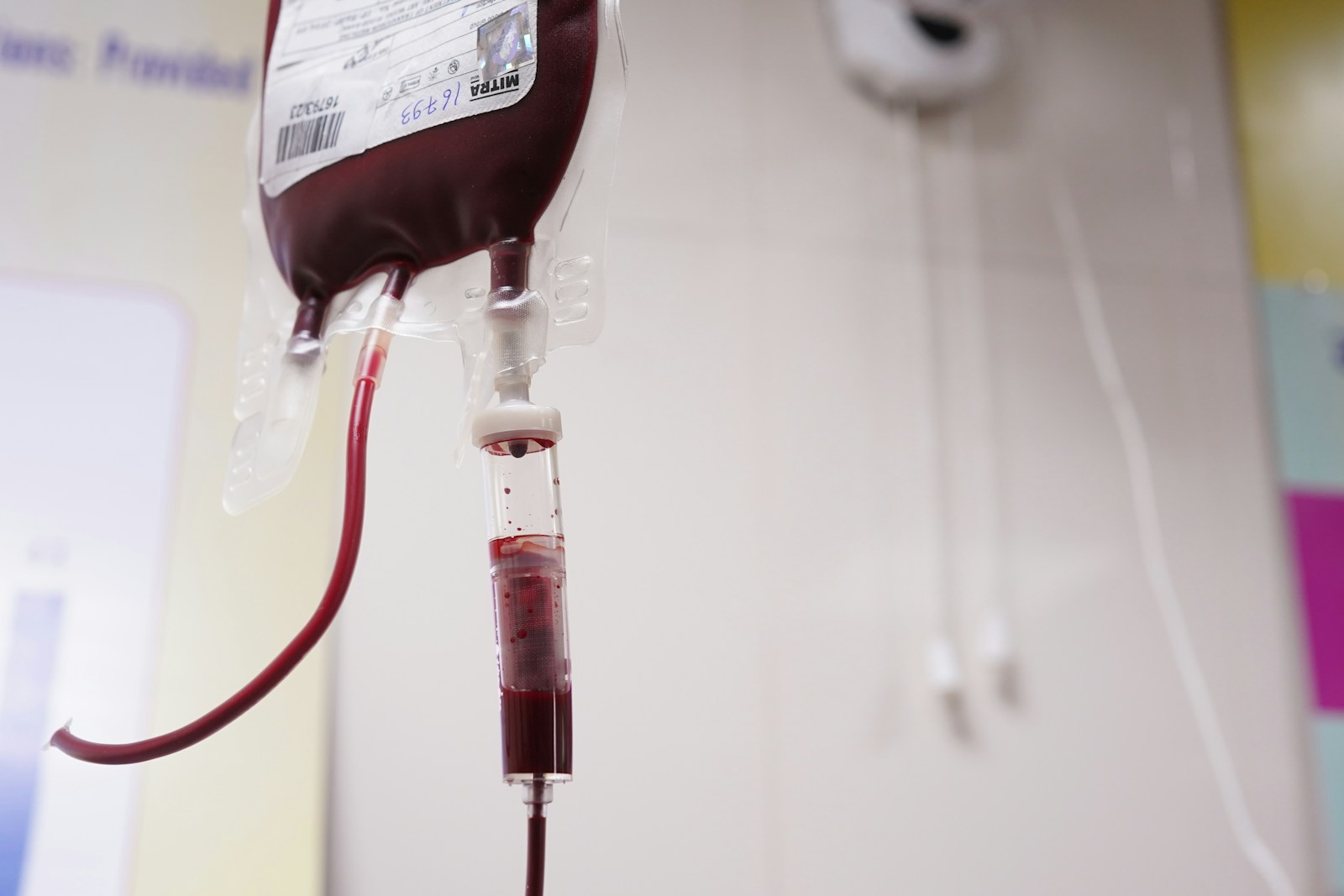
Blood Transfusion: Benefits and Potential Dangers
Blood transfusion is a life-saving medical procedure that involves transferring blood or blood components from one person (the donor) to another (the recipient). This practice has been crucial in modern medicine, especially in treating patients with severe injuries, blood disorders, or during major surgeries. While blood transfusions offer immense benefits, they also come with certain risks. Understanding the advantages and potential dangers of blood transfusion is essential for making informed decisions in medical settings. This article will explore both aspects to give a comprehensive overview of this important medical procedure.
The Process of Blood Transfusion
Before diving into the benefits and dangers, it’s important to understand the basic process involved in blood transfusion. The procedure begins with collecting blood from a donor. This blood is then carefully tested, processed, and stored for future use. When a patient needs a transfusion, the stored blood is cross-matched with the recipient’s blood type to ensure compatibility. Blood transfusion can involve whole blood, but more commonly, specific components of blood are used, such as:
- Red Blood Cells (RBCs): These are primarily used to treat patients with anemia or severe blood loss.
- Plasma: This component is used to treat patients with clotting disorders, burns, or liver diseases.
- Platelets: These are crucial for patients who have low platelet counts, often due to cancer treatments or bone marrow conditions.
- Cryoprecipitate: A component of plasma, cryoprecipitate is used to treat patients with bleeding disorders like hemophilia.
Now that we understand the process, let’s delve into the benefits and potential risks of blood transfusion.
Benefits of Blood Transfusion
1. Saving Lives in Emergencies
One of the most significant benefits of blood transfusions is the ability to save lives in emergency situations. Patients who experience severe blood loss due to trauma, surgery, or childbirth can quickly become critically ill if their body doesn’t receive enough oxygen. Red blood cells are essential in transporting oxygen throughout the body, and in the case of significant blood loss, a transfusion can rapidly restore the necessary oxygen levels. Without a timely transfusion, such patients could suffer irreversible damage to organs or even death.
2. Treatment of Blood Disorders
Blood transfusions are vital for patients with chronic blood disorders such as sickle cell disease or thalassemia. These conditions affect the body’s ability to produce healthy red blood cells, leading to severe anemia. Regular transfusions can help maintain normal hemoglobin levels, allowing patients to lead healthier lives with reduced symptoms. For many individuals with these disorders, blood transfusions are a lifelong necessity.
3. Support During Major Surgeries
During major surgical procedures, especially those that involve the heart, liver, or brain, patients may lose a significant amount of blood. Blood transfusions ensure that the patient maintains adequate blood volume and oxygen delivery during and after the procedure, helping to prevent complications such as organ failure. Surgeons often rely on transfusions to keep patients stable during complex operations.
4. Treatment for Cancer Patients
Patients undergoing chemotherapy or radiation therapy for cancer often experience a drop in blood cell counts, especially red blood cells and platelets. These treatments can suppress bone marrow function, leading to anemia and an increased risk of bleeding. Blood transfusions help replenish these cells, reducing symptoms like fatigue, shortness of breath, and the risk of life-threatening hemorrhages.
5. Management of Severe Anemia
Anemia, characterized by a low red blood cell count, can result from various causes, including chronic kidney disease, nutritional deficiencies, or bone marrow disorders. Severe anemia can lead to extreme fatigue, weakness, and cardiovascular issues. In such cases, blood transfusions can rapidly restore red blood cell levels, improving the patient’s quality of life and reducing the risk of complications.
6. Treatment for Bleeding Disorders
Patients with bleeding disorders such as hemophilia or von Willebrand disease may require transfusions of specific blood components like plasma or cryoprecipitate. These transfusions provide essential clotting factors that help control bleeding, whether from an injury, surgery, or spontaneous internal bleeding. Without these transfusions, patients with severe bleeding disorders would face life-threatening complications from even minor injuries.
7. Improvement in Maternal Health
Pregnancy and childbirth are times when women are at risk of significant blood loss. Postpartum hemorrhage is a leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide. Blood transfusions play a critical role in managing severe blood loss during childbirth, ensuring that new mothers can recover without complications. As a result, transfusions have significantly improved maternal survival rates, particularly in regions where access to advanced medical care is limited.
8. Better Quality of Life for Patients with Chronic Conditions
For patients with chronic illnesses that cause ongoing blood loss or hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells), such as gastrointestinal bleeding or autoimmune disorders, regular blood transfusions can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being. These transfusions allow patients to maintain better energy levels, reduce the risk of complications, and enjoy a higher quality of life.
Potential Dangers of Blood Transfusion
While blood transfusions provide many life-saving benefits, they are not without risks. It is crucial to consider the potential dangers before undergoing a transfusion. In most cases, these risks are minimized through careful screening and monitoring, but they can still occur.
1. Allergic Reactions
Some patients may experience allergic reactions to a blood transfusion. This can happen even when the blood is a perfect match for the recipient’s blood type. Common symptoms of an allergic reaction include itching, hives, and fever. In rare cases, a more severe reaction known as anaphylaxis can occur, causing difficulty breathing, swelling, and a drop in blood pressure. Immediate medical attention is required in such cases.
2. Fever and Chills
After a transfusion, some patients develop a fever, accompanied by chills and discomfort. This reaction, known as a febrile non-hemolytic reaction, occurs when the recipient’s immune system reacts to white blood cells or other proteins in the donor blood. While these symptoms are usually mild and resolve on their own, they can be distressing for the patient. In some cases, premedication with antipyretics (fever-reducing medications) can help prevent this reaction.
3. Hemolytic Reactions
One of the most serious potential dangers of blood transfusion is a hemolytic reaction, which occurs when the recipient’s immune system attacks the transfused red blood cells. This can happen if the blood types are not compatible, leading to the destruction of the donor red blood cells. Hemolytic reactions can cause symptoms such as back pain, dark urine, jaundice, and in severe cases, kidney failure or death. To prevent hemolytic reactions, thorough cross-matching of blood types is performed before transfusions.
4. Transmission of Infections
Despite rigorous screening processes, there is still a small risk of transmitting infections through blood transfusions. Bloodborne pathogens such as HIV, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and syphilis can be transmitted if donor blood is contaminated. However, in most developed countries, stringent testing protocols have dramatically reduced this risk. For example, in the United States, the risk of contracting HIV from a blood transfusion is estimated to be less than 1 in 1.5 million.
5. Iron Overload (Hemochromatosis)
For patients who require frequent blood transfusions, such as those with sickle cell disease or thalassemia, there is a risk of iron overload. Each transfusion introduces more iron into the body, and over time, this can lead to a dangerous buildup of iron in organs like the liver, heart, and pancreas. Iron overload can cause serious complications such as liver disease, heart problems, and diabetes. To manage this risk, patients may need to undergo regular blood tests to monitor their iron levels and may require treatment with iron-chelating agents, which help remove excess iron from the body.
6. Graft-Versus-Host Disease (GVHD)
Graft-versus-host disease is a rare but serious complication of blood transfusions. It occurs when the donor’s immune cells attack the recipient’s tissues. This condition is more common in patients with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or organ transplantation. Symptoms of GVHD include skin rashes, liver dysfunction, and gastrointestinal problems. To reduce the risk of GVHD, blood for transfusion is often irradiated to eliminate the donor’s immune cells.
7. Lung Injury (TRALI)
Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) is a rare but life-threatening complication that can occur within hours of receiving a transfusion. It is caused by an immune reaction that damages the lungs, leading to symptoms such as difficulty breathing, low oxygen levels, and fluid buildup in the lungs. TRALI requires immediate medical intervention, and patients typically receive supportive care such as oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation.
8. Circulatory Overload (TACO)
Transfusion-associated circulatory overload (TACO) occurs when too much blood is transfused too quickly, causing the recipient’s heart to become overwhelmed. This can lead to symptoms such as shortness of breath, high blood pressure, and fluid buildup in the lungs. TACO is more likely to occur in patients with heart or kidney problems, and careful monitoring of transfusion volume and speed can help prevent this complication.

Mitigating Risks of Blood Transfusion
Given the potential dangers, healthcare providers take several precautions to minimize the risks associated with blood transfusions. These include:
- Careful Blood Typing and Cross-Matching: To prevent hemolytic reactions, blood is meticulously cross-matched to ensure compatibility between the donor and recipient.
- Blood Screening: All donated blood undergoes extensive testing for infectious diseases, reducing the risk of transmission.
- Use of Pre-Medication: Patients who are at risk of allergic reactions or febrile reactions may receive pre-medications to prevent these issues.
- Monitoring: Patients receiving transfusions are closely monitored for signs of complications, such as allergic reactions or lung injury. Immediate intervention can prevent severe outcomes.
- Irradiation of Blood Products: For patients at risk of GVHD, blood products are irradiated to eliminate immune cells that could cause harm.
Conclusion
Blood transfusions remain a cornerstone of modern medicine, offering life-saving benefits to millions of patients worldwide. From treating trauma victims to managing chronic diseases, transfusions have transformed patient care. However, like any medical procedure, they come with risks. By understanding both the benefits and potential dangers of blood transfusions, patients and healthcare providers can work together to make informed decisions, ensuring that the life-saving advantages of this procedure are realized while minimizing the risks.
The careful selection of blood donors, rigorous testing protocols, and advanced medical interventions have made blood transfusions safer than ever before. Yet, ongoing research and technological advancements continue to improve the process, aiming to further reduce risks and enhance the safety and efficacy of transfusions for all patients.
If you or a loved one is facing a medical condition that may require a blood transfusion, it’s essential to have an open conversation with your healthcare provider. Make sure you understand both the potential benefits and the risks involved to make the best decision for your health.
Keywords: blood transfusion risks, blood transfusion benefits, complications of blood transfusion, blood transfusion process, life-saving blood transfusion, side effects of blood transfusion
Please share this blog if you found it helpful!
Author bio:
My name is Dr. Marat Kazak. I have been working as a professional Podiatrist serving Northern California community since 2014. My extensive medical and surgical knowledge combined with an ongoing curiosity to learn about the latest trends define my success in the field of foot, ankle and leg medical and surgical care.
The goal of this website is to give you the tools to better care for yourself, to dispel medical myths, and to empower you with information to save time and money! If you are looking for an answer on foot and ankle pain, this is the place to find it. If you do not see your topic of interest covered, please send me a message and I will do my best to discuss it thoroughly in my next upcoming post.
Visit this blog often to learn about latest developments, treatments, and approaches to healing and recovery!